
The local time within a time zone is defined by its offset (difference) from Coordinated Universal Time (UTC), the world's time standard. In day-to-day speak, however, the time zone is often referred to as just Eastern Time, regardless of whether it's standard or Daylight Saving Time.

However, during DST, the city is on Eastern Daylight Time (EDT), which is 4 hours behind UTC (UTC–4). What is a time zone? Time Zone Name Changesĭuring DST, the local time zone name and abbreviation changes, usually to include either “daylight” or “summer” in the time zone name.įor example, New York's standard time is Eastern Standard Time (EST), which is 5 hours behind UTC (UTC–5). Most European countries are on standard time 5 months of the year and spend 7 months on DST. In the US and Canada, for instance, the standard time period is only around 4.5 months. The standard time period is often shorter than the DST period. The periods of standard time and DST are not equally long. The remaining countries use DST during the summer months, generally setting clocks forward one hour from standard time. More than 60% of the countries in the world use standard time all year.
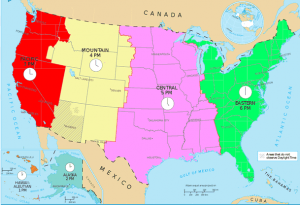
Standard time is sometimes referred to as or winter time or normal time, while DST may also be called summer time, especially in the UK.ĭST changes: Dates and local times No DST in Most Countries Standard time is also known as winter time or normal time.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
